Spice Up Your Health: Discovering Saffron's Incredible Benefits
The Golden Spice of Wellness🌺
Hey there, health enthusiasts! 🌟 Have you ever wondered about the magic hidden in your spice rack? Let's zoom in on one extraordinary spice – Saffron. Known for its vibrant colour and unique flavour, Saffron is a culinary delight and a powerhouse of health benefits. In this friendly chat, we're diving deep into how Saffron can improve your well-being.

Why Saffron? Saffron, often called 'red gold', isn't just a fancy spice for your paella; it's packed with goodies for your body and mind. This little spice has significant benefits, from brightening your mood to fighting inflammation.
Mood Booster Extraordinaire: Feeling blue? Saffron's here to the rescue! With properties akin to antidepressants, it's like sunshine in a spice. We'll explore how this cheerful buddy can lift your spirits. 😊
A Warrior Against Inflammation Chronic inflammation is a buzzkill for the body. But guess what? Saffron's anti-inflammatory magic is like a peace treaty for your cells. We'll delve into how this spice keeps the inflammation monster at bay.
Cognitive Champion Saffron's not just pretty; it's smart too! Boosting brain power is one of its secret superpowers. We'll uncover how it keeps your memory sharp and attention on point. 🧠
The Promise of Saffron: A Sneak Peek
We're just getting started! From heart health to digestive wellness, Saffron wears many hats. Stay tuned as we unravel more secrets of this golden wonder. Whether you're a health guru or just curious about natural remedies, you're in for a treat. Let's embark on this saffron-scented journey together and uncover how a pinch of this spice can make a world of difference to your health. 🌿✨
The Antidepressant Effects of Saffron: A Natural Mood Lifter 🌞

Saffron: Your Natural Cheerleader 🌼
Ever heard the saying, "A pinch of saffron is worth a thousand smiles"? It might be more accurate than you think! With its vibrant hue, Saffron isn't just a feast for the eyes; it's a natural mood booster.
Saffron's antidepressant properties are like a hidden treasure in those delicate threads. It's packed with bioactive compounds like crocin and Safranal that have a knack for lifting spirits. Think of it as a gentle, natural pick-me-up, perfect for when you need extra sunshine.
Nature's Answer to Antidepressants 💊 vs. 🌿
Now, let's talk about Saffron versus prescription antidepressants. It's like comparing a gentle breeze to a strong wind. Prescription antidepressants, while effective, often come with a luggage of side effects – from weight gain to feeling a bit zombified (you know what I mean!). Saffron, on the other hand, is more like a natural, side-effect-free companion. It's like having a friend who always knows how to cheer you up without any downsides!
Saffron Extract Reduces Stress and Improves Low Mood in Healthy Individuals
Studies Show: Saffron Brings Smiles 😊
Let's get a bit of science here (but in a fun way, I promise!). Various studies have put Saffron to the test, and guess what? It passed with flying colours! One fascinating study published in the Journal of Behavioral and Brain Science found that Saffron significantly improved mood in participants compared to a placebo. It's like a happiness booster in a spice!
Another study in the Journal of Affective Disorders compared Saffron with a popular antidepressant, fluoxetine. The results? Saffron was just as effective in reducing depressive symptoms but with fewer side effects. It's like discovering that your favourite comfort food is good for you!
Effects of Saffron Extract Supplementation on Mood
Real People, Real Results 🙌
But it's not just about what happens in the lab. People who've added a sprinkle of Saffron to their diets have noticed the difference. From feeling more upbeat to having a brighter outlook on life, the anecdotes align with science. It's like Saffron is throwing a little party for your brain cells!
Mental and physical effects of a saffron
Saffron: A Ray of Hope in Mental Health
It's incredible to think that a spice used in cooking can profoundly affect our mental well-being. Whether struggling with the blues or looking for a natural mood enhancer, Saffron might be the golden ticket.
Embracing Saffron: A Step Towards Happier Days
So, how can you incorporate this mood-lifting miracle into your life? It's easy! You can add Saffron to your meals, sip on saffron-infused teas, or even explore supplements (chat with your doctor first!).
Final Thoughts: Spice Up Your Mood with Saffron
To wrap it up, Saffron isn't just a luxury spice; it's a beacon of hope for those seeking natural ways to enhance their mood. It's a gentle, effective, and joyous addition to anyone's wellness toolkit. So, next time you're feeling down, a little saffron might be what you need to light up your day! 🌟Saffron's Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: Nature's Firefighter 🚒🌿
Understanding the Blaze of Chronic Inflammation 🔥
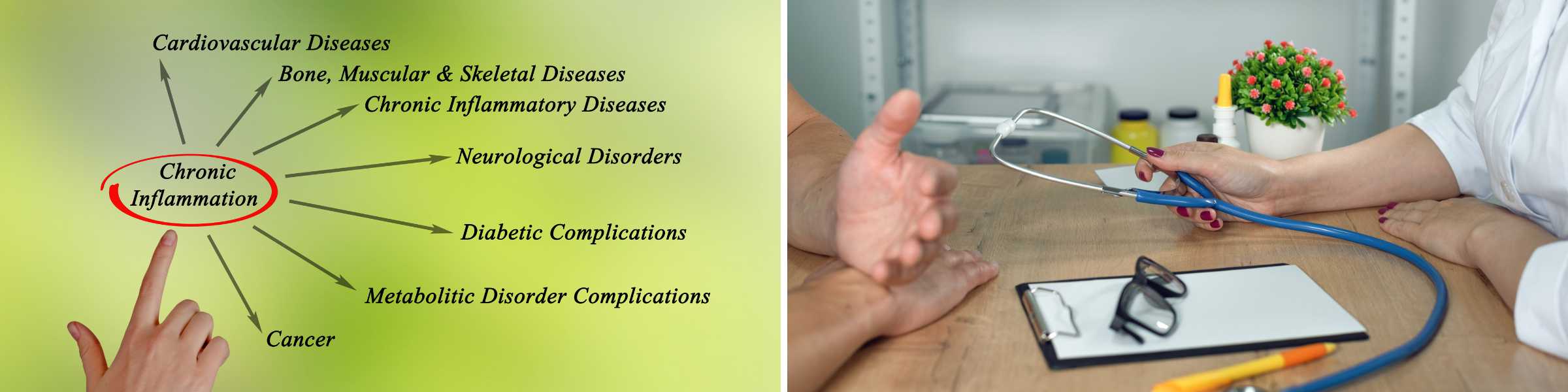
Let's start with a background check on our not-so-friendly visitor, chronic inflammation. Imagine your body's immune system is like a well-trained firefighter, always ready to extinguish small fires (aka injuries or infections). But sometimes, these firefighters get overzealous and keep fighting even when the fire's out. This leads to chronic inflammation – a sneaky, ongoing blaze that can cause all sorts of trouble, from arthritis to heart disease and even some forms of cancer. It's like a silent alarm constantly ringing in the body, and you want it switched off!
Saffron to the Rescue! 🚨➡️🌸
Enter Saffron, our golden hero! This precious spice is like a calming influence on the overactive firefighters. It contains potent compounds like crocin, crocetin, and Safranal, which act like a soothing balm on inflammation. It's like having a super-efficient fire extinguisher that's all-natural and smells fantastic!
Science Speaks: Saffron's Anti-Inflammatory Credentials 📊
Now, let's don our lab coats and peek into some research. A study published in the "Journal of Pharmacopuncture" showed that Saffron could significantly reduce inflammation markers in the body. It's scientific proof that Saffron is not just a pretty face!
Another research piece in the "Journal of Translational Medicine" highlighted how crocin, one of Saffron's star compounds, effectively reduces inflammation in brain cells. This isn't just good news; it's excellent news, especially for anyone keen on keeping their brain as healthy as their body.
Anti-inflammatory properties of drugs from saffron crocus
Real-Life Impact: More Than Just Numbers 🌟
But hey, it's not all about lab results and numbers. People who've added Saffron to their diets have reported feeling less 'inflamed', more comfortable, and generally healthier. It's like getting a wellness boost with every pinch of this golden spice.
Embracing Saffron's Anti-Inflammatory Magic 🧙♂️✨
Incorporating Saffron into your life is as easy as sprinkling fairy dust. Add it to your teas and dishes, or even explore supplements. A little goes a long way in calming the internal fires and keeping chronic inflammation at bay.
Saffron: Your Delicious Anti-Inflammatory Ally 🍲
To wrap this up, consider Saffron your delicious ally in the battle against chronic inflammation. It's not just an exotic ingredient for your kitchen; it's a potent, health-boosting spice that brings flavour and wellness to your life. So, the next time you're cooking up a storm, sprinkle in some saffron and think of the goodness it's adding, not just to your dish but to your body, too! 🌈
Saffron's Role in Cognitive Health: A Brain-Boosting Delight 🧠✨

The Brainy Side of Saffron: Cognitive Enhancer 🌟
Step aside, brain puzzles and memory games, and make way for the extraordinary spice in the cognitive arena – Saffron! This isn't just your average kitchen ingredient; it's a secret weapon for your brain health. With its unique compounds, Saffron steps in like a wise sage for your neurons, boosting memory, attention, and overall cognitive function.
Saffron vs. Cognitive Decline: The Battle for Brain Power 🤺
As we age, our brain cells start to feel the weight of time, leading to a decline in cognitive functions. But here's where saffron swings into action. Its natural compounds, particularly crocin and Safranal, have shown promising effects in protecting and rejuvenating these cells. It's like a spa treatment for your brain, keeping it youthful and agile.
Studies Speak: Saffron's Brain-Boosting Evidence 📚
Diving into the pool of scientific research, we find some exciting revelations. A "Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics" study found that Saffron could improve cognitive function in Alzheimer's patients. It's not just a sprinkling of hope; it's a full-blown potential game-changer for those grappling with cognitive challenges.
Another research, published in the "Journal of Psychopharmacology," highlighted Saffron's potential in enhancing memory and learning abilities. It's like having a natural tutor for your brain, helping it stay sharp and focused.
Saffron for mild cognitive impairment and dementia
Making Saffron a Part of Your Cognitive Diet 🥘
Incorporating Saffron into your daily routine can be as simple as adding a pinch to your tea or meals. It's not just about savouring its flavour; it's about feeding your brain with nature's goodness.
Conclusion: Saffron, A Spice for a Smarter You 🌈
In conclusion, Saffron isn't just about adding zest to your dishes; it's a powerful ally for cognitive health. Whether you're looking to boost or support your brain power as you age, Saffron offers a natural, delicious way to keep your cognitive functions in shape. So next time you see those delicate threads, remember you're looking at a brain-boosting powerhouse!
Saffron in Cardiovascular Health: A Heart's Best Friend 💖

Saffron: The Heart-Healthy Spice 🌹
When caring for our hearts, the solutions are often found in the most unexpected places - like in Saffron, the vibrant spice known for its unique flavour. But beyond its culinary uses, Saffron is emerging as a champion for cardiovascular health. It's not just a spice; it's a heart-whisperer!
Lowering Blood Pressure Naturally with Saffron 💓
High blood pressure is a silent threat, creeping up unnoticed. It's a significant risk factor for heart disease and stroke. But here's the good news: Saffron has shown promising results in bringing those numbers down. The active compounds in Saffron, such as crocetin, act like a gentle nudge, encouraging your blood vessels to relax and your heart to beat a bit more peacefully. It's like a soothing melody for your cardiovascular system.
A Shield Against Heart Disease and Stroke 🛡️
The fight against heart disease and stroke requires a robust defence, and Saffron is well-equipped for the battle. By reducing blood pressure and possessing antioxidant properties, Saffron helps keep the arteries clear and the blood flowing smoothly. It's like having a personal bodyguard for your heart.
The Scientific Backing: Saffron's Cardio Credentials 📖
Let's peek into the research world to solidify Saffron's heart-healthy claims. Studies, such as those published in the "Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology," have highlighted Saffron's potential in improving cardiovascular health. Another study in the "Journal of Clinical Hypertension" pointed out Saffron's effectiveness in reducing blood pressure, offering a natural alternative to conventional medication.
The cardiovascular-protective properties of saffron
Embracing Saffron for a Happy Heart ❤️
Incorporating Saffron into your daily diet can be a delightful and easy step towards better heart health. A little Saffron keeps your heart beating joyfully, whether in your morning tea, your favourite dish, or as a supplement.
Conclusion: Saffron - The Heart's Spice Companion 🌠
In summary, Saffron isn't just a kitchen staple; it's a powerful ally in maintaining cardiovascular health. With its natural ability to lower blood pressure and reduce heart disease risks, Saffron offers a simple yet effective way to keep your heart happy and healthy. So, the next time you sprinkle Saffron into your cooking, remember that you're enhancing flavour and giving your heart some love!
Digestive Health and Saffron: A Tummy-Loving Treat 🍲

Saffron: A Time-Honored Digestive Aid 🌿
With its golden threads, Saffron has long been a secret weapon in the world of digestive wellness. Traditionally, it was not just a prized spice for its flavour but also for its ability to soothe the stomach. From the aromatic kitchens of ancient Persia to modern-day health enthusiasts, Saffron has always had a place in promoting digestive health.
Modern Understanding: Saffron's Role in Digestion 🧠
In today's fast-paced world, our digestive systems often bear the brunt of our hectic lifestyles. Enter Saffron, nature's own digestive aid. This isn't just about old wives' tales; modern science backs up what traditional healers have known for centuries. Saffron helps smooth processes, easing blouses and promoting bowel movements. It's like having a calming whisper for your tummy.
The Gut-Friendly Benefits of Saffron 🌟
But how exactly does Saffron work its magic? Its anti-inflammatory properties play a significant role. Inflammation is often a culprit behind digestive discomfort. Saffron, with its natural anti-inflammatory prowess, helps keep the digestive tract in a happy state. Moreover, its antioxidant qualities mean it's not just fighting today's digestive battles but also protecting your gut for the future.
The Science Behind the Spice 📚
Let's dive into some research to give this conversation more clout. Studies, such as one published in the "World Journal of Gastroenterology," have shown that Saffron can positively impact digestive health. Another study in the "Journal of Ethnopharmacology" supported Saffron's role in improving digestion and relieving gastrointestinal discomfort.
Saffron: The Golden Spice with Therapeutic Properties on Digestive Diseases
Embracing Saffron for Digestive Bliss 🥄
Incorporating Saffron into your diet is delightfully simple. A pinch in your tea or favourite dish adds flavour and works behind the scenes to keep your digestive system running smoothly.
Conclusion: Saffron, Your Digestive System's New Best Friend 🌈
In conclusion, Saffron's benefits for digestive health are as accurate as they are ancient. This vibrant spice is not just about adding colour to your meals; it's a powerful ally for your digestive system, offering natural and effective relief. So next time you reach for the Saffron, remember, you're not just cooking; you're caring for your digestive health!
Saffron for Eye Health: A Visionary Spice 👁️✨
Illuminating the Eyes with Saffron's Magic 🌟
Saffron, the vibrant and aromatic spice, is a treat for your taste buds and a blessing for your eyes. Among its many health benefits, Saffron plays a significant role in maintaining and improving eye health. The key players are two of Saffron's most potent compounds: crocin and Safranal.
Crocin and Safranal: Saffron's Eye-Protecting Duo 👀
Crocin and Safranal are like the dynamic duo of eye health. Crocin, known for giving Saffron its distinctive golden colour, is a powerful antioxidant. It helps protect the eyes from harmful oxidative stress, a critical factor in various eye conditions. On the other hand, Safranal lends Saffron its unique aroma and packs a punch in protecting the eyes. Together, they work in harmony to shield and enhance your vision.
Review of Evidence for the Usage of Antioxidants for Eye Aging
A Guard Against Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) 🛡️
One of the most remarkable benefits of Saffron for the eyes is its potential to prevent age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a leading cause of vision loss. AMD primarily affects the macula, the part of the eye responsible for central vision. As we age, the macula can deteriorate. Still, Saffron's powerful antioxidants rescue us, helping maintain the structure and function of this crucial eye part.
Saffron therapy for the treatment of mild/moderate age-related macular degeneration
The Science of Seeing: Research on Saffron and Eye Health 📖
Research into Saffron's effects on eye health has produced some promising findings. A study published in the "Journal of Translational Medicine" showed that regular consumption of Saffron could improve vision in those suffering from AMD. Another study in the "Pharmacological Research" journal found that Saffron not only helps slow the progression of AMD but may also improve retinal function in the early stages of the condition.
The role of saffron in improvement of ocular surface disease
Embracing Saffron for Brighter, Healthier Eyes 🌈
Incorporating Saffron into your diet could be a simple yet effective way to contribute to the overall health of your eyes. Whether adding a few strands to your tea or cooking with it regularly, Saffron provides a natural, flavorful way to support your vision.
Conclusion: Saffron, A Feast for the Eyes 🌹
In summary, Saffron's benefits extend beyond its culinary uses, offering a natural means to support and protect your eyesight. With its potent compounds, crocin and Safranal, Saffron stands out as a valuable ally in maintaining eye health and potentially preventing age-related ailments. So the next time you see those little red strands, remember, they're not just for flavour; they're a feast for your eyes!
Boosting Immunity with Saffron: Your Wellness Shield 🛡️🌺

Saffron: The Immune System's Natural Ally 🌟
Nature often holds the key in the quest for a robust immune system, and Saffron is one of its most vibrant secrets. This golden spice is a culinary delight and a powerful booster for your immune system. With its unique blend of bioactive compounds, Saffron is a natural defender against various health challenges.
Saffron's Arsenal Against Infections and Diseases 🦠
Saffron is a versatile warrior in the body's battle against infections and diseases. Its immune-boosting properties stem from its rich antioxidant content, which includes crocin, crocetin, and Safranal. These compounds don't just stand guard; they actively engage in the fight against invading pathogens, bolstering the body's defences.
The Triple Threat: Antiviral, Antibacterial, Antifungal 🌿
The beauty of Saffron lies in its multifaceted approach to boosting immunity. It's not just about strengthening the body's defences; it's also about its antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal properties. Saffron's components have been shown to inhibit the growth of various bacteria and fungi, offering a broad spectrum of protection. Regarding viral infections, Saffron's compounds interfere with viral replication, providing an additional layer of defence.
Backed by Science: Saffron's Immune-Boosting Evidence 📚
The immune-enhancing effects of Saffron are more than just folklore. Scientific research supports its role in immune health. A study published in the "Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry" highlighted Saffron's ability to enhance immune response. Another research in the "International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents" showed Saffron's effectiveness against certain bacteria and fungi, showcasing its potential as a natural antimicrobial agent.
Saffron: A Promising Natural Therapeutic and Immune-Boosting Agent
Embracing Saffron for a Stronger Immune System 💪
Incorporating Saffron into your daily routine is a simple yet effective step towards boosting your immune system. Whether through culinary uses or as a supplement, saffron adds flavour, colour, and a dose of good health.
Conclusion: Saffron, A Spice for Immunity and Beyond 🌈
In conclusion, Saffron goes beyond its role as a spice, emerging as a valuable ally in maintaining and enhancing immune health. Its blend of antioxidant, antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal properties makes it a unique and natural way to keep your body's defences strong. So, next time you enjoy a dish with saffron, remember that you're not just treating your taste buds but also fortifying your immune system!
Scientific Research and Emerging Benefits of Saffron: Unveiling Nature's Secrets 🌟

Delving into the World of Saffron Research 🧪
Saffron, long cherished for its culinary and medicinal properties, is now catching the eye of the scientific community. Recent studies are shedding light on this golden spice, revealing a spectrum of health benefits that were previously uncharted. From its traditional uses to cutting-edge research, Saffron is proving to be a treasure trove of wellness.
Saffron's Fight Against Cancer: A Ray of Hope 🎗️
Among the most promising areas of saffron research is its potential in combating cancer. Scientists have been intrigued by Saffron's anticarcinogenic properties. Compounds like crocin and Safranal in Saffron have been found to inhibit the growth of cancer cells and induce apoptosis (cell death) in various cancer types, including leukemia, ovarian carcinoma, and colorectal cancer. It's as though Saffron is a natural sentinel, guarding our cells against cancerous changes.
Neuroprotection: Saffron's Brain-Boosting Power 🧠
Another emerging benefit of Saffron is its neuroprotective effects. This goes beyond its cognitive-enhancing properties; Saffron shows the potential to protect the brain from neurodegenerative disorders. Studies suggest that its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties can help combat oxidative stress and inflammation, which play a role in diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Saffron is not just nourishing the brain today; it's safeguarding it for tomorrow.
Historical Wisdom and Modern Science: A Confluence 🌉
Historically, Saffron has been used for a myriad of ailments, ranging from digestive issues to mood disorders. What's fascinating is how modern research validates these ancient practices, bridging the gap between traditional wisdom and scientific understanding. Current research trends focus on understanding how Saffron's active compounds interact at the molecular level to confer these health benefits.
Conclusion: Saffron, a Spice of the Past, Present, and Future 🌅
In conclusion, saffron continues to be a subject of interest in scientific circles, with each study unveiling new aspects of its health benefits. From its anti-cancer potential to neuroprotective effects, Saffron stands at the intersection of historical use and modern science, offering a promising and natural approach to health and wellness. As research continues to evolve, it's clear that Saffron's story is far from over; it's a spice that has transcended time, bringing ancient wisdom into the future.
Saffron health Benefits FAQ's:
What are the main health benefits of Saffron?
-
Saffron is known for its antioxidant properties, mood enhancement, potential anti-cancer properties, and ability to improve heart health, memory & respiratory diseases.
Can Saffron help improve mood and treat depressive symptoms?
-
Yes, studies suggest that Saffron can help improve mood and treat mild to moderate depressive symptoms, possibly due to its influence on serotonin and other mood-related neurotransmitters.
Is saffron beneficial for eye health?
-
Yes, Saffron contains antioxidants like crocin and crocetin, which are believed to protect against oxidative stress and may improve vision in age-related macular degeneration.
Can Saffron help with weight loss?
-
Some research indicates that saffron may help people lose weight by reducing appetite and curbing cravings. However, more extensive studies are needed for conclusive evidence.
Does Saffron have anti-cancer properties?
-
Preliminary studies suggest that Saffron might have anti-cancer properties due to its antioxidant content and the ability to inhibit the growth of cancer cells, but more research is required.
How does Saffron benefit heart health?
-
Thanks to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, Saffron may benefit heart health by reducing risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Can saffron improve memory and cognitive function?
-
Some studies indicate that Saffron could improve memory and cognitive function, particularly in Alzheimer's disease, possibly due to its antioxidant effects.
Is Saffron effective in treating sexual dysfunction?
-
Saffron has shown potential in treating sexual dysfunction, particularly in improving erectile function in men and sexual arousal in women, though more research is needed.
Can Saffron help in the treatment of menstrual symptoms?
-
Saffron may help alleviate menstrual symptoms like pain, PMS, and irregularity due to its antispasmodic and anti-inflammatory properties.
Is Saffron safe for everyone to use?
-
Saffron is generally safe when consumed in culinary amounts. However, in high doses, it can be toxic. Pregnant women and individuals with certain health conditions should consult a healthcare provider before using saffron supplements.
Learn more about Saffron’s Health Benefits and Risks





























